ErlangB is used to work out how many lines are required if the traffic figure (in Erlangs) during the busiest hour known. The Erlang B distribution is based on the following assumptions:
- Holding times are constant and exponential
- Blocked cells are cleared
- Calls are taken in random order
- There are an infinite number of sources
To use the Erlang B forecasting method:
- Click on
 and open the ForecastX_Erlang.xls file.
and open the ForecastX_Erlang.xls file.
Note: The ForecastX_Erlang.xls file is a data example to demonstrate how the Erlang B method is used. For your company’s purposes, you will have your own data available. - Click on the Erlang B1 sheet.
- Click in a cell containing data and open ForecastX by clicking on
 . ForecastX displays with the Data Capture tab open.
. ForecastX displays with the Data Capture tab open. 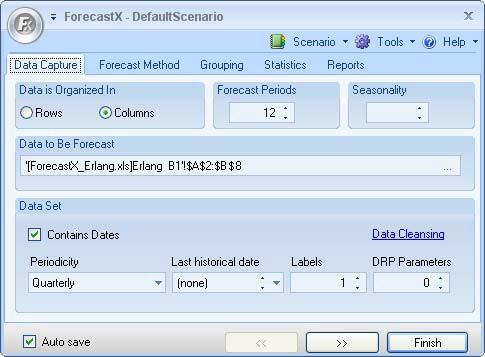
- In the Forecast periods area, type in 4 to forecast for the next four quarters.
- Click on the Forecast Method tab.
- In the Forecast Technique area, scroll through the list of methods and select Erlang B. The Erlang B Forecasting technique displays.
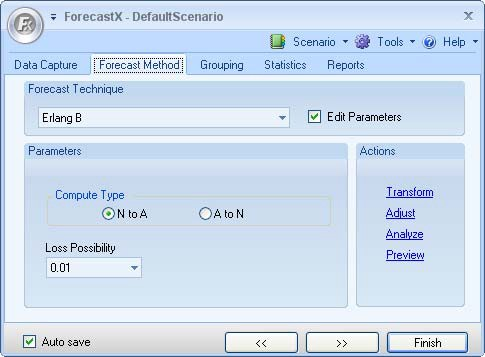
- Select Edit parameters to activate Erlang B’s parameters.
- In the Compute Type area, select either N to A, or A to N. N means the number of servers, and A means traffic measured by Erlang B. Select N to A.
- In the Lost Possibility area, select one of the options for the percentage of loss that is possible.
- Click Finish.
As you review the results within the standard report, notice how ForecastX has forecasted the number of servers needed for the next 4 quarters, and ForecastX has also given the traffic levels (A).